November Rollup
/
RAG Search: Low-Hanging Fruit for RAG Search
jxnl.co
Author: Jason Liu
Date: 2024/05/11
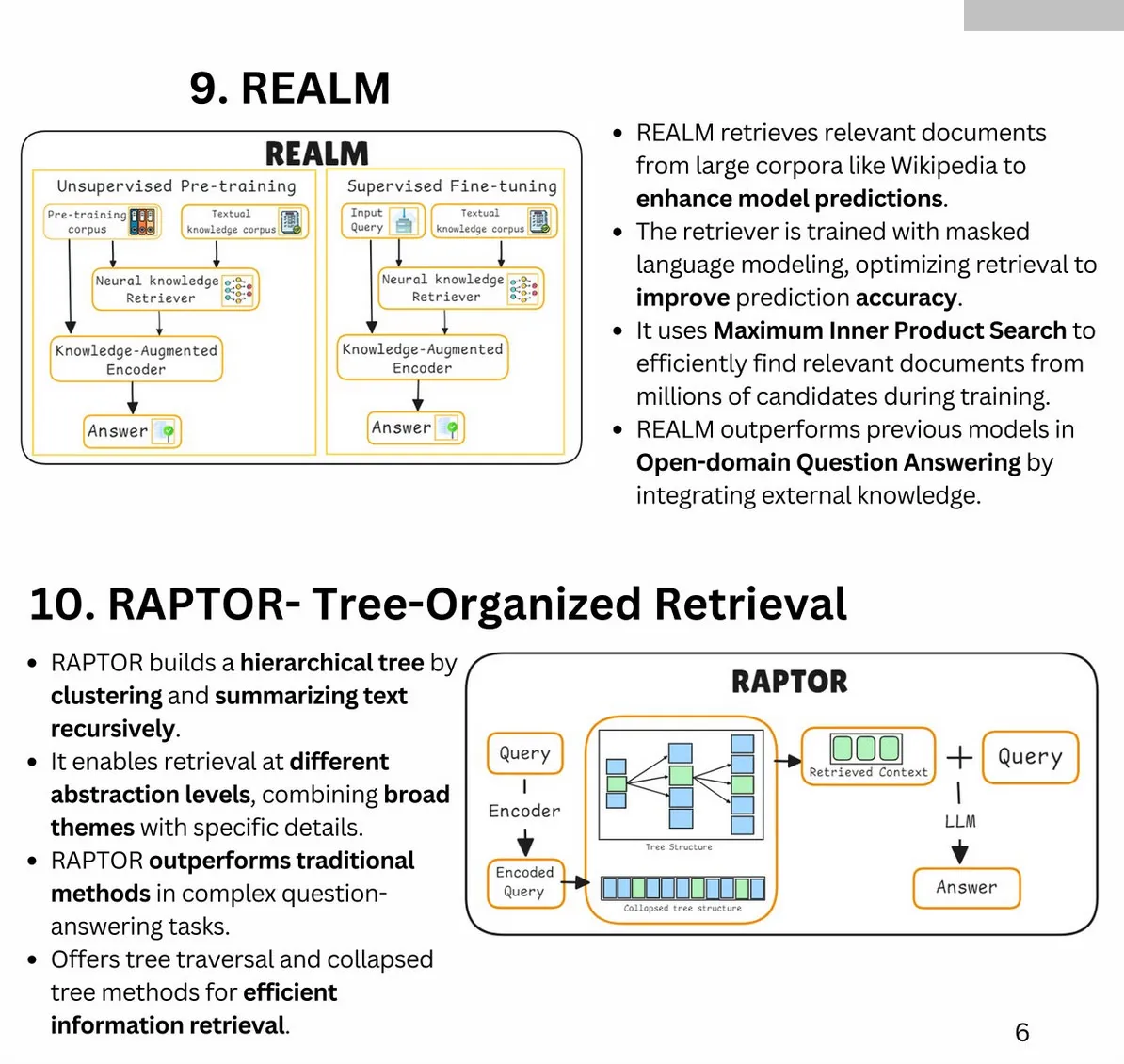
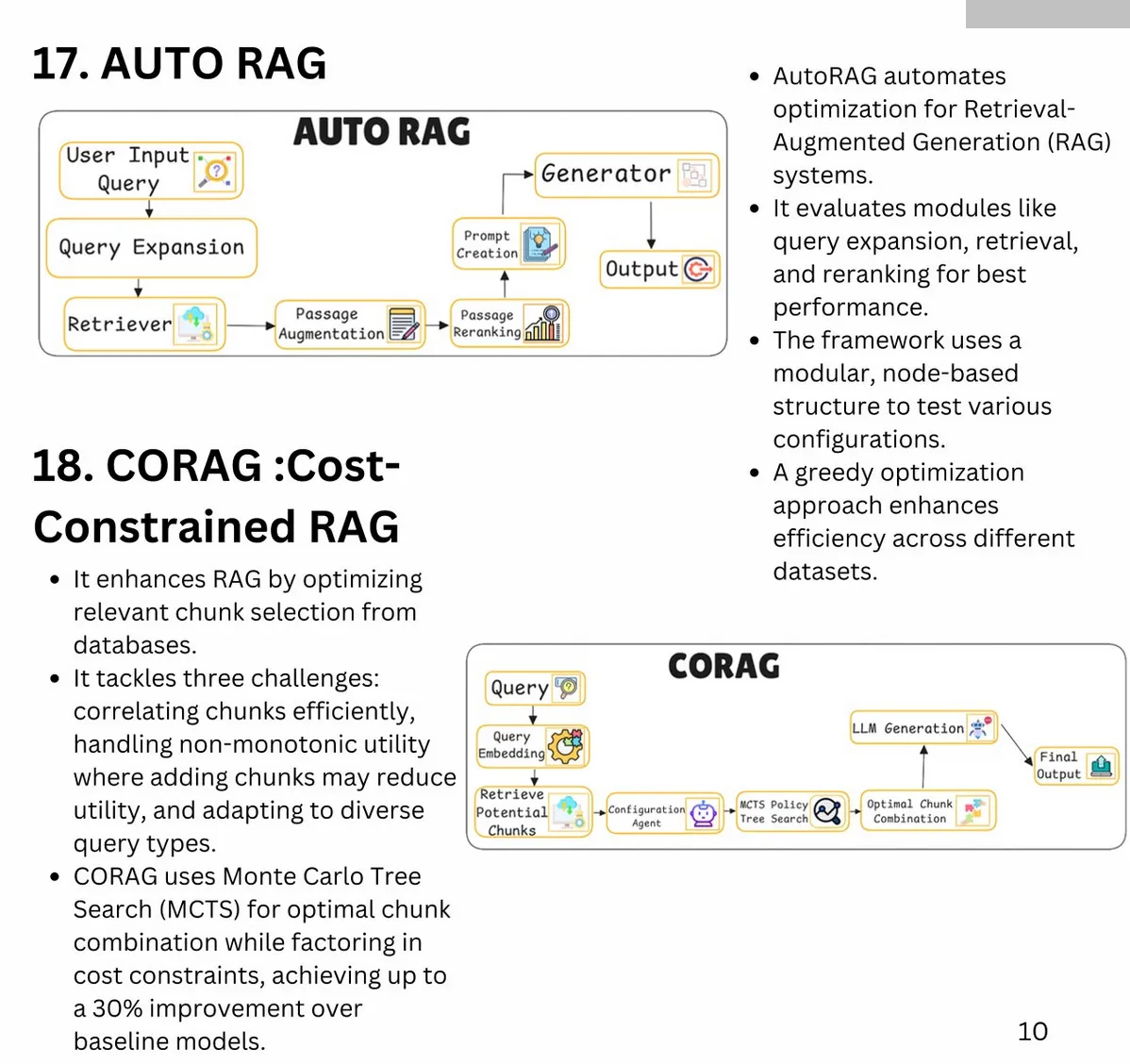
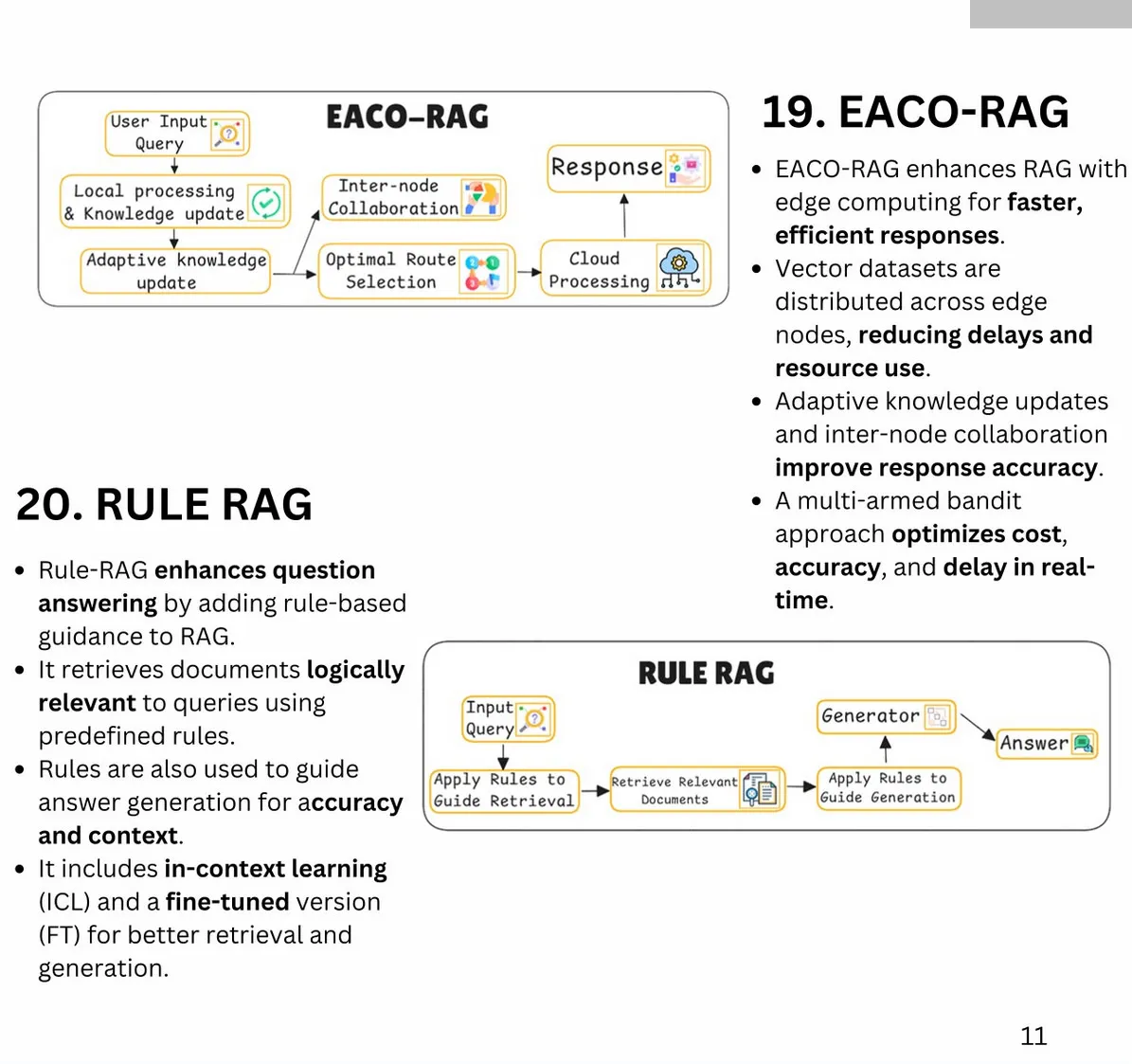
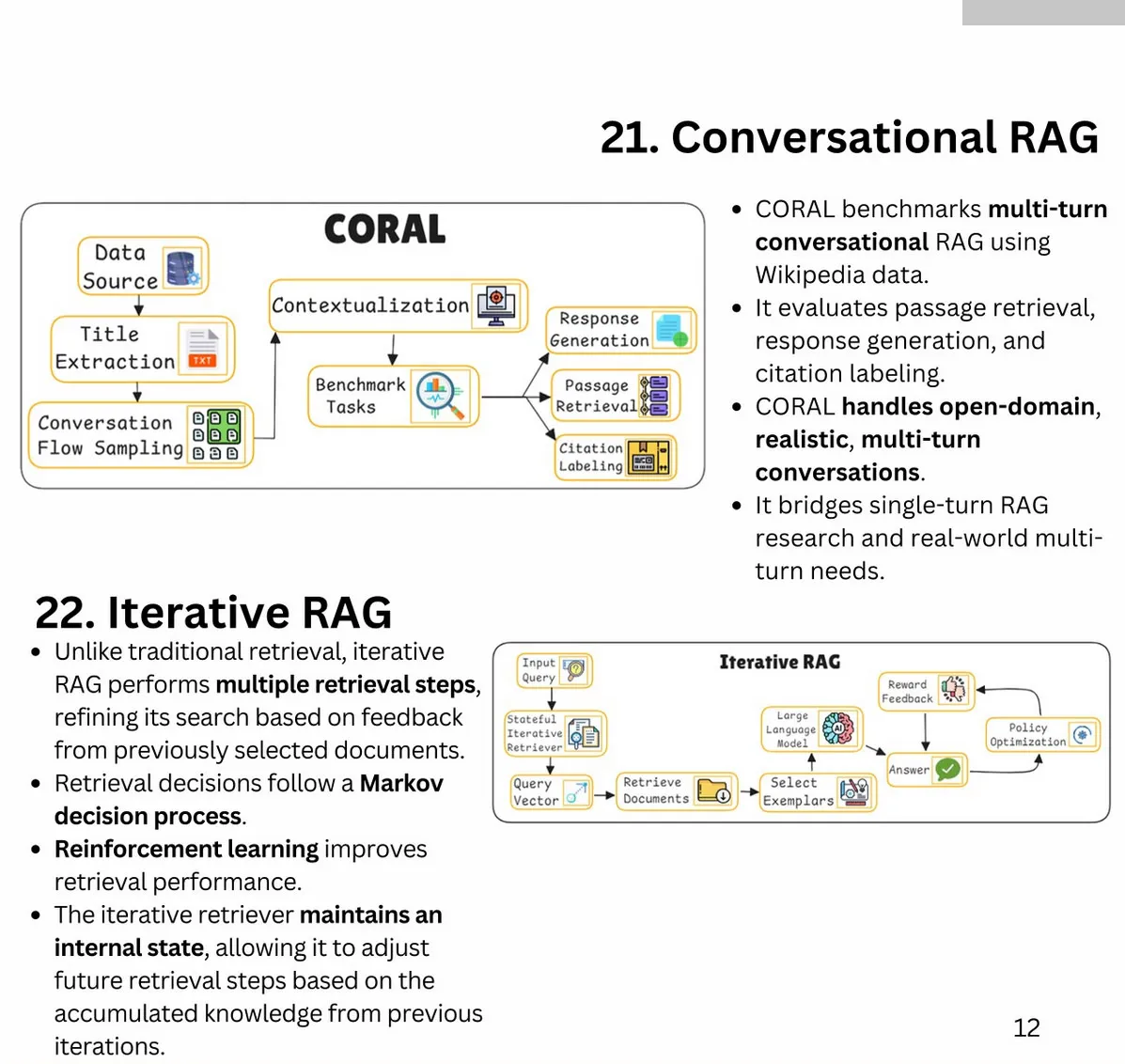
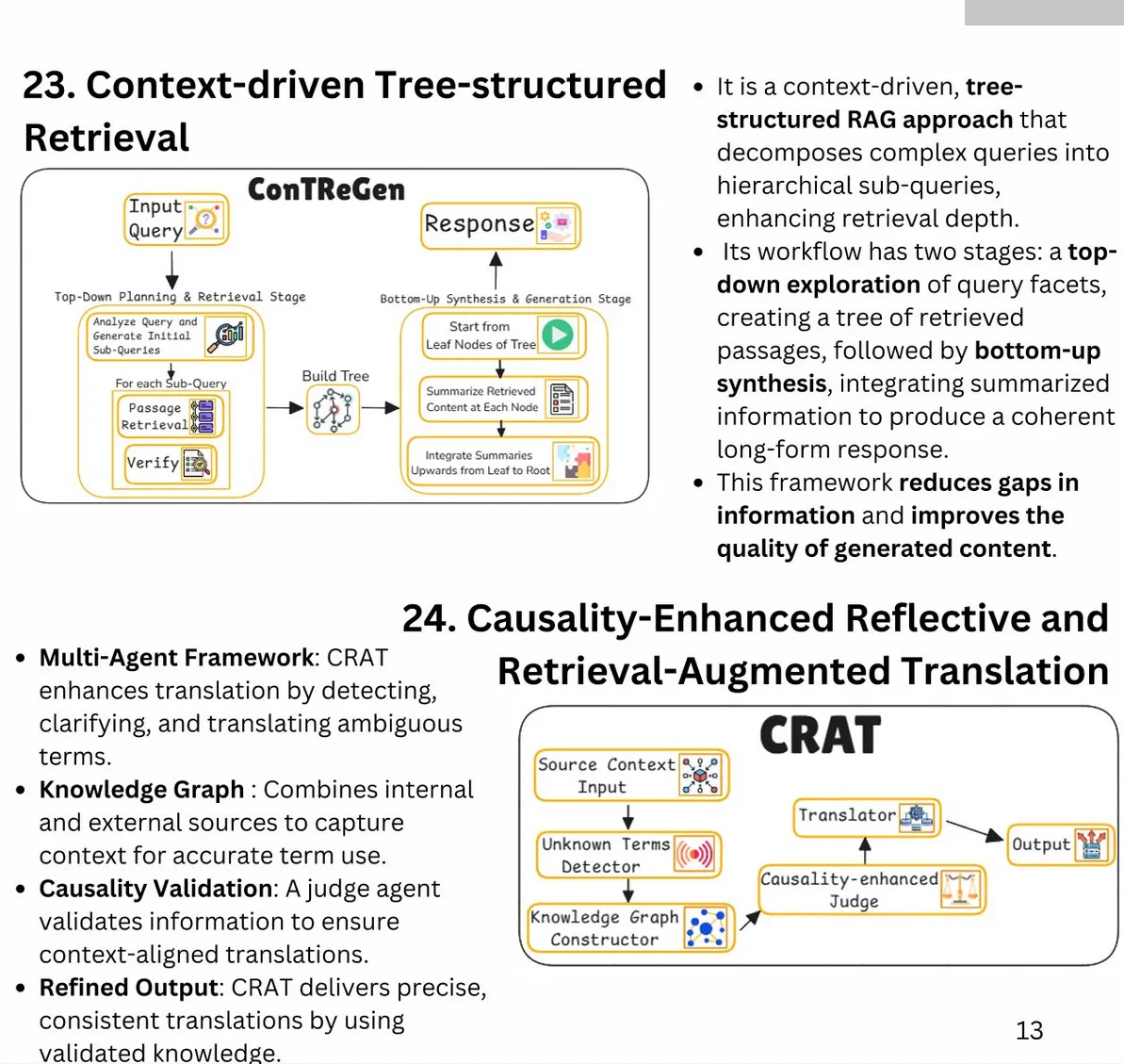
Key Improvements for RAG Search Systems:
-
Synthetic Data for Baseline Metrics:
- Generate synthetic questions from text chunks to establish precision and recall baselines.
- Enables repeatable, low-cost testing and system evaluation.
-
Tracking Average Cosine Distance and Cohere Reranking Score:
- Log metrics to analyze query performance and identify areas for improvement. Once you have a table of query and scores, you will be able to do data analysis to figure out areas where you are underperforming.
- Example schema includes request ID, cosine distance, and reranking scores.
-
Using Full-Text Search:
- Combine BM25 with semantic search for better results.
- Tools like LanceDB1 enhance user experience.
-
Making Text Chunks Look Like Questions:
- Pre-format chunks as questions to align embeddings and reduce runtime latency.
-
Including File and Document Metadata:
- Append metadata (e.g., title, tags, author, path, dates) to text chunks for richer search results.
Notable Resources:
- Systematically Improving RAG Applications Course – A 4-week course covering advanced retrieval techniques and evaluation.
- Free RAG Crash Course – Six email series on improving RAG systems.
RAG: 25 Types of RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
linkedin.com
Author: Bhavishya Pandit
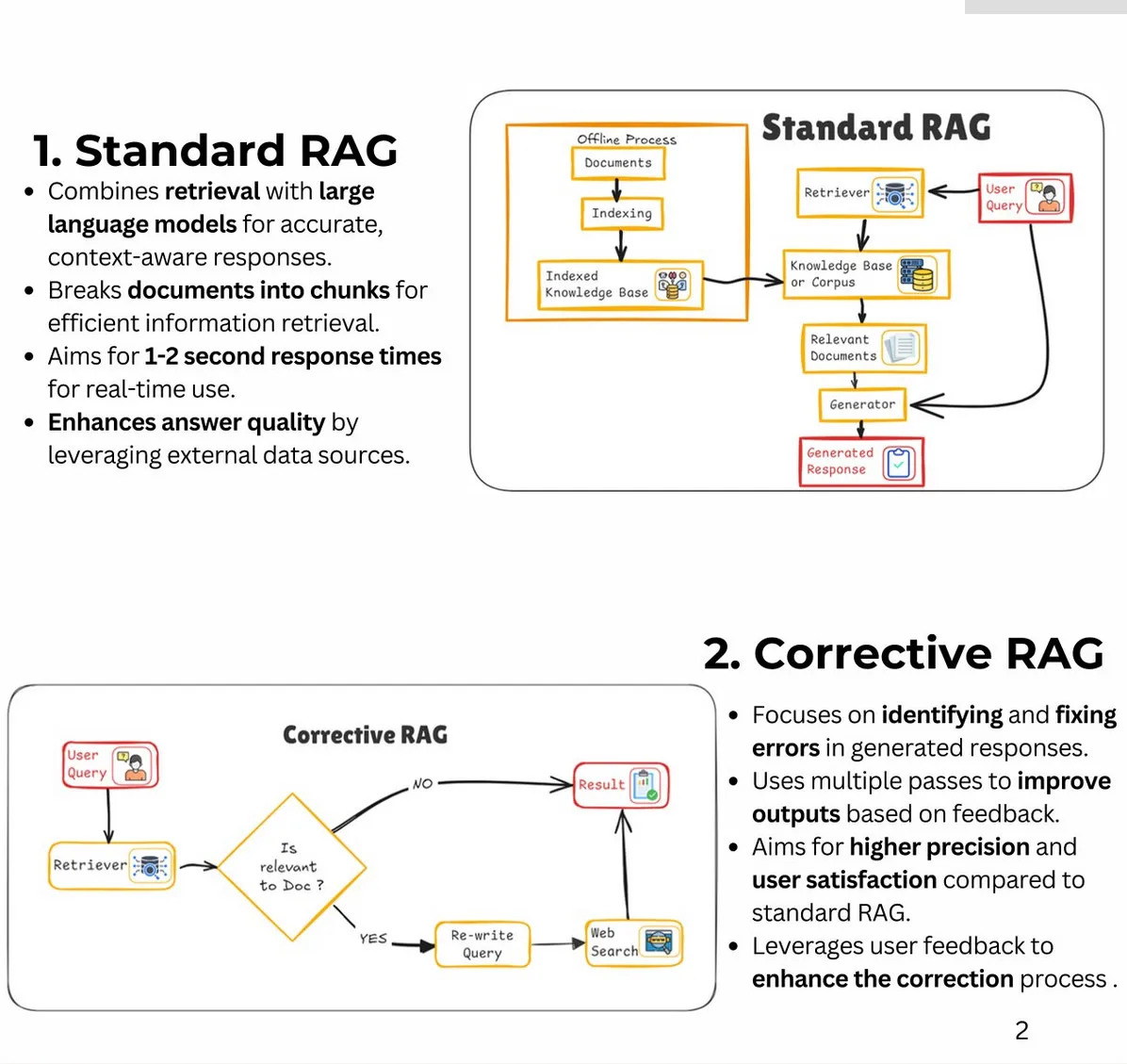
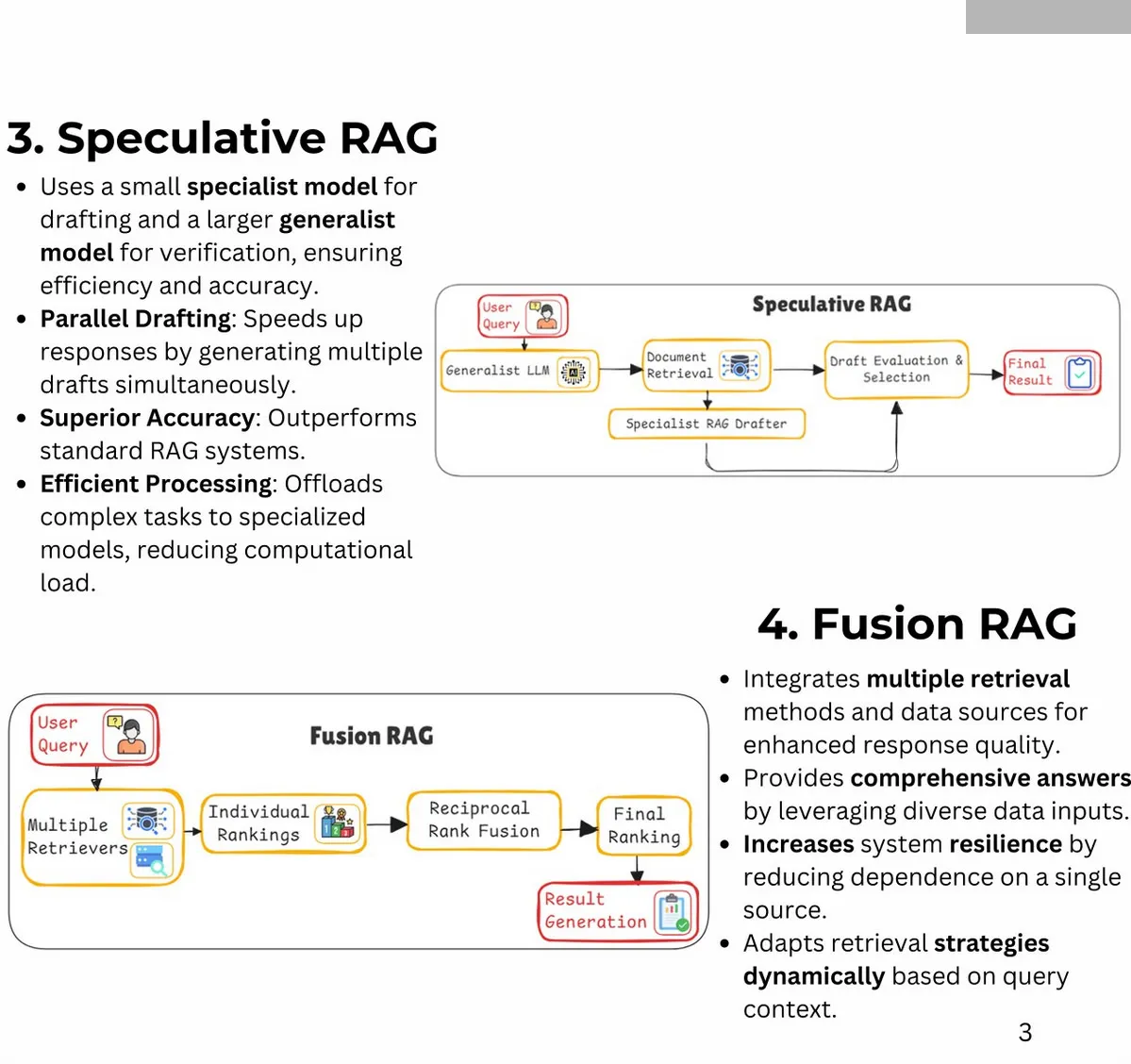
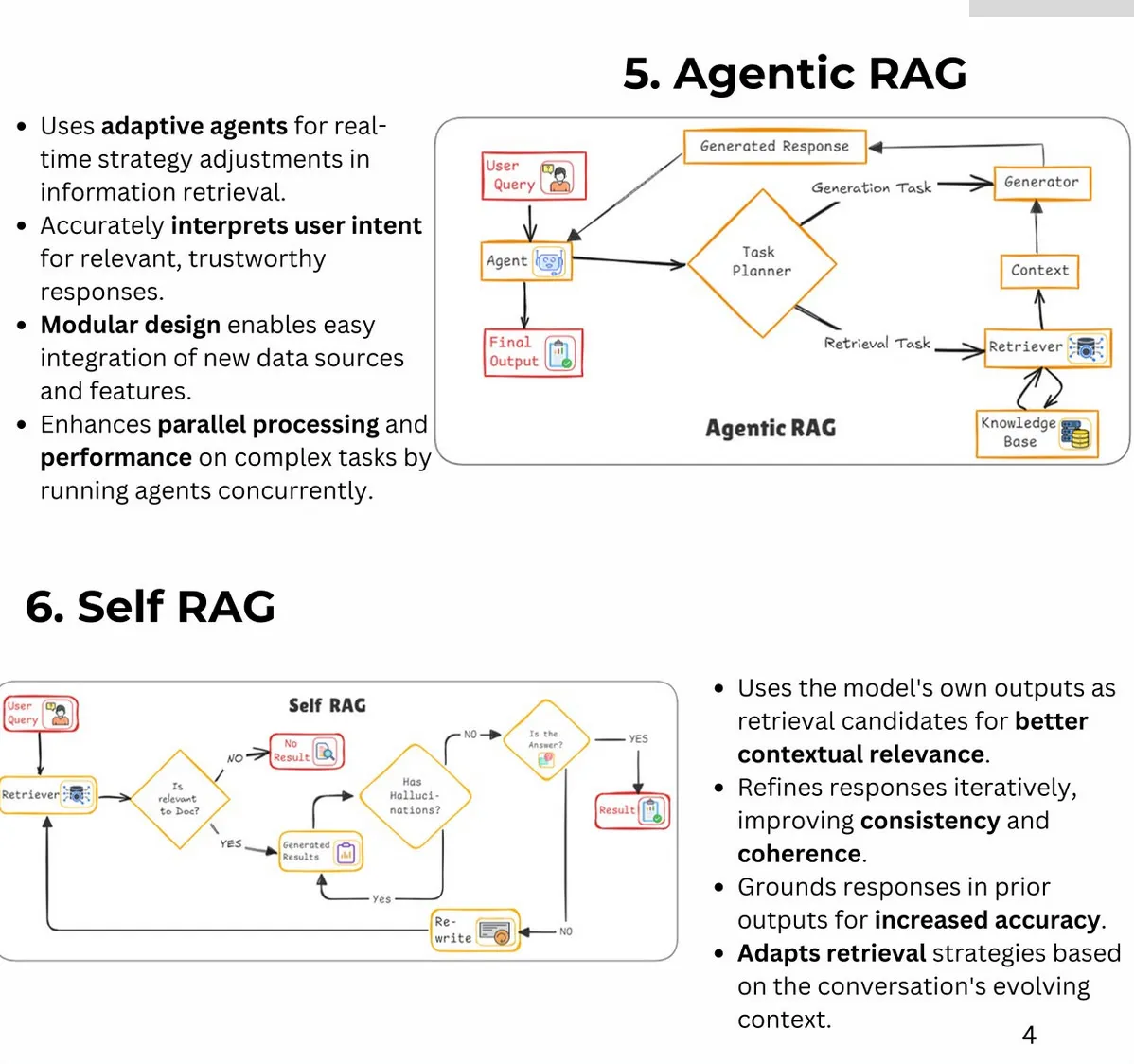
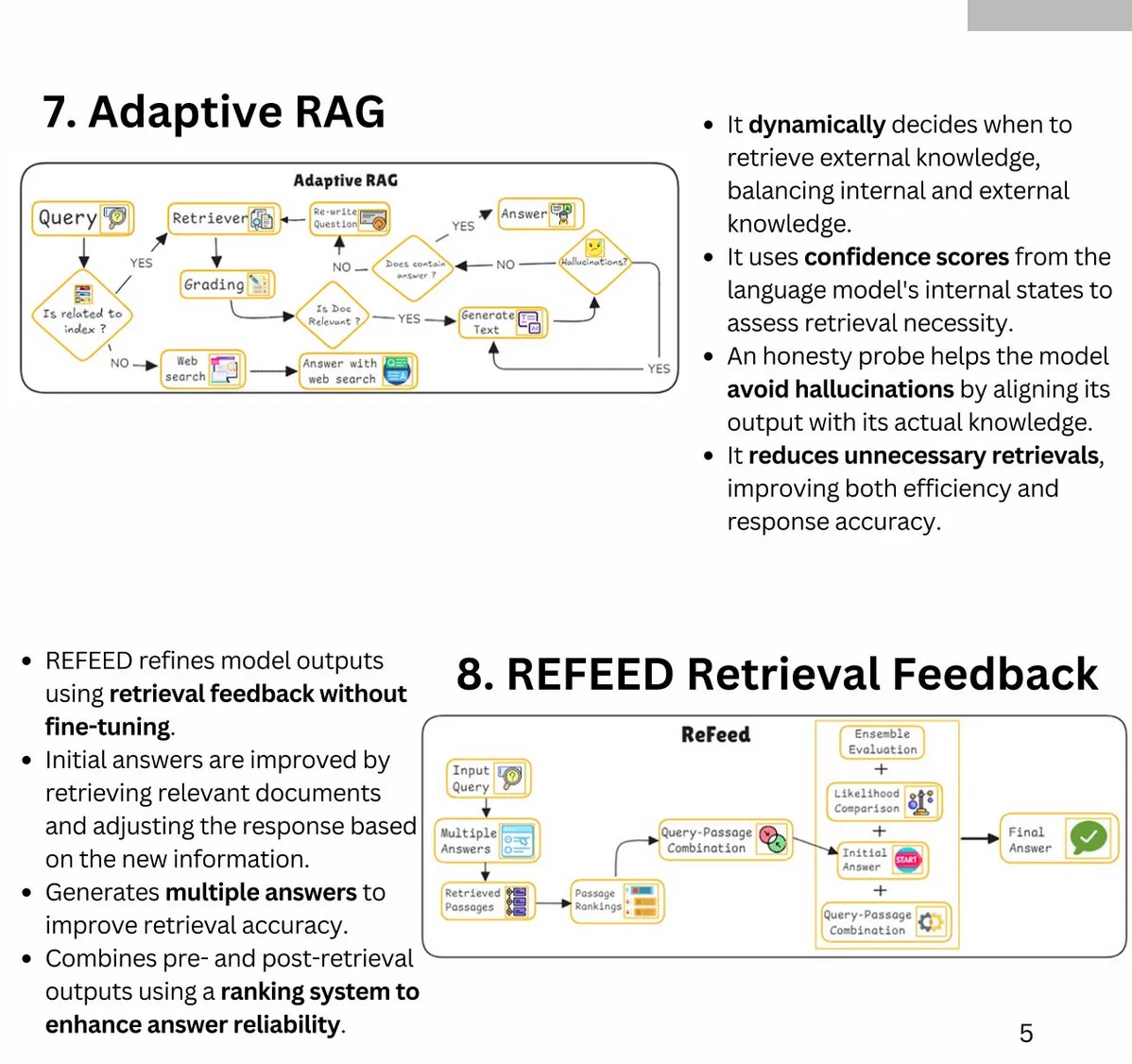
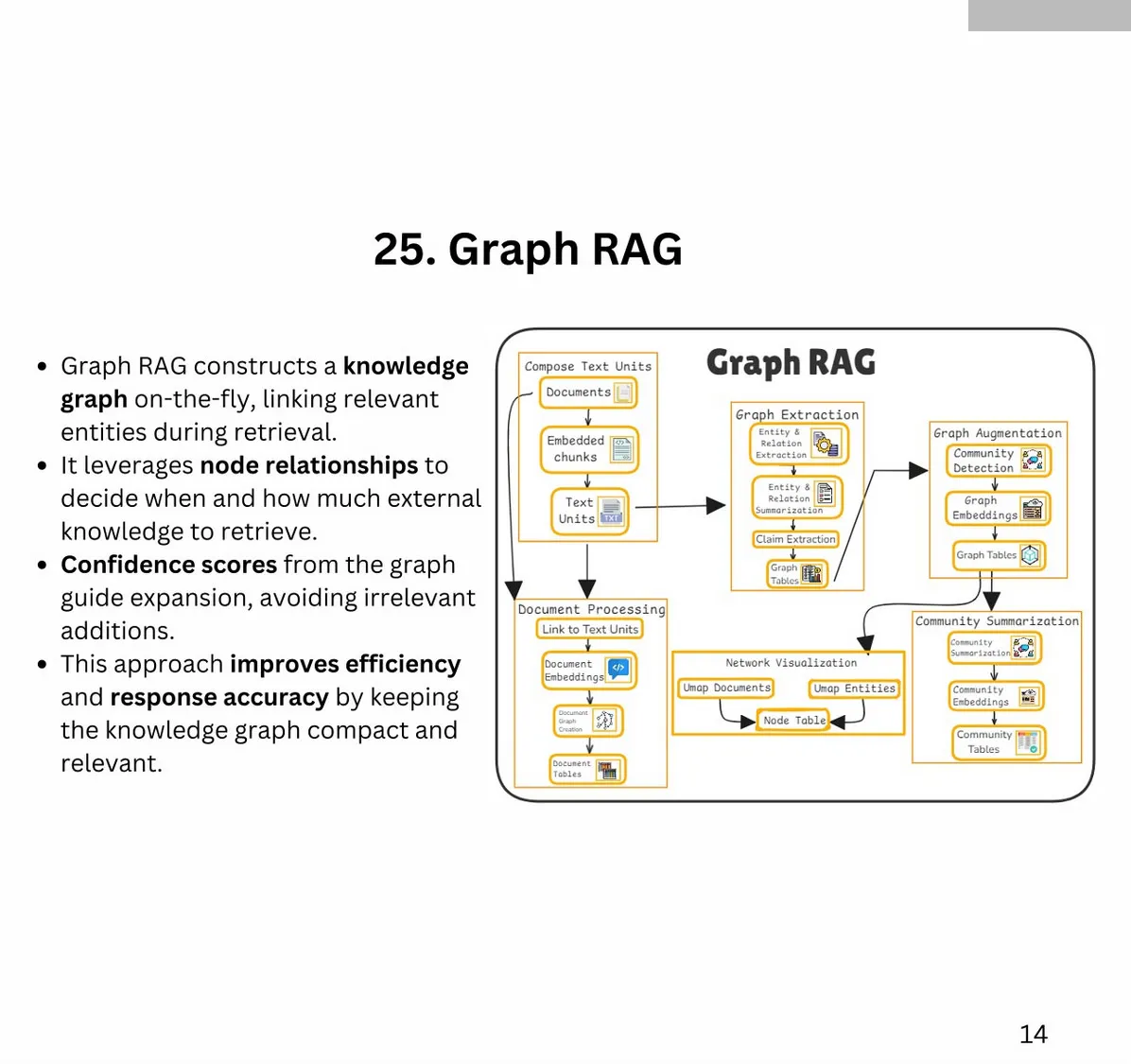
- Additional Types: Fast Graph RAG, Light RAG, Nano Graph RAG, Contextual RAG, Multi-Source RAG, Hierarchical RAG, Multi-pass RAG, Feedback-based RAG, Adversarial RAG, Hybrid RAG, RePLUG, ATLAS
Lesser-Known Frameworks to Build Your RAG System
linkedin.com
Author: Shantanu Ladhwe
-
RAGFlow: Focused on document understanding with grounded citations, explainable chunking, and seamless data integration.2 GitHub
-
Cognita: Scales from prototype to production, offers modular components, no-code UI, and incremental indexing.3 GitHub
-
STORM by Stanford: Designed for creating Wikipedia-like articles with humans in the loop, ideal for collaborative knowledge curation.4 GitHub
-
FlashRAG: Python toolkit with benchmarks and RAG algorithms, supporting preprocessing, indexing, and efficient execution.5 GitHub
-
LLM-App: Builds scalable RAG applications with live indexing, multimodal pipelines, and SQL Q&A.6 GitHub
-
R2R: Bridges experimentation and deployment with multimodal ingestion, hybrid search, and observability tools.7 GitHub
Comments:
-
Franck Stéphane NDZOMGA: Suggests optimizing RAG pipelines with PostgreSQL and pgvector; drops unnecessary abstractions.8 Blog
-
Michael Trimmel: Appreciates R2R for enabling GraphRAG prototyping without Neo4J.9
-
Christopher Danz: Recommends Microsoft’s GraphRAG for graph-based RAG. GitHub
-
Chakka Guna Sekhar: Highlights a multi-modal RAG chatbot project that integrates visual information for user proofs.10 App | GitHub
Notable Machine Learning Papers
-
ViT Efficiency Analysis:
- Paper: Reassesses Vision Transformers (ViT) against newer models using the same training setup.
- Insight: Original ViT remains Pareto optimal in accuracy vs. cost for some metrics, despite numerous alternatives.
-
Mechanistic Interpretability:
- Paper: Focuses on mechanistic interpretability, predicted to popularize the next significant research trend.
- Comment: Anthropic’s work draws attention to the internal behavior of transformers.
-
Taylor Series Approximation for ML:
- Paper: Links MLPs and self-attention to Taylor Series.
- Insight: Highlights theoretical relations between function approximation in physics/math and ML architectures.
-
Energy Transformers:
- Paper: Derives transformer-like architectures from modern Hopfield networks.
- Practical Use: Simplifies theoretical understanding and implementation of transformers for image generation.
-
The AI Scientist:
- Paper: Proposes a step toward more autonomous AI agents in scientific discovery.
-
Sparse Autoencoder Geometry:
- Paper: Explores sparse autoencoders’ ability to create geometric structures in high-dimensional space, aligning AI design with cognitive organization.
Controversial or Bold Predictions
- Return of RNNs:
- Debated relevance and potential comeback of RNNs due to theoretical properties like infinite recursion.
- Suggested fusion with transformers for new architectures.
Additional Mentions
-
QLora (NeurIPS 2023):
- Paper: Quantization of LoRA, highly cited but debated impact.
-
Diffusion Models Optimization:
- Paper: Nvidia’s work on enhancing diffusion models with EMA and hypersphere-constrained weights.
Emerging Themes
- Cross-disciplinary applications (physics/math insights into ML).
- Importance of mechanistic interpretability and sparse representations.
- Debate on theoretical frameworks vs. practical innovations.
Resources Captured1112131415161718
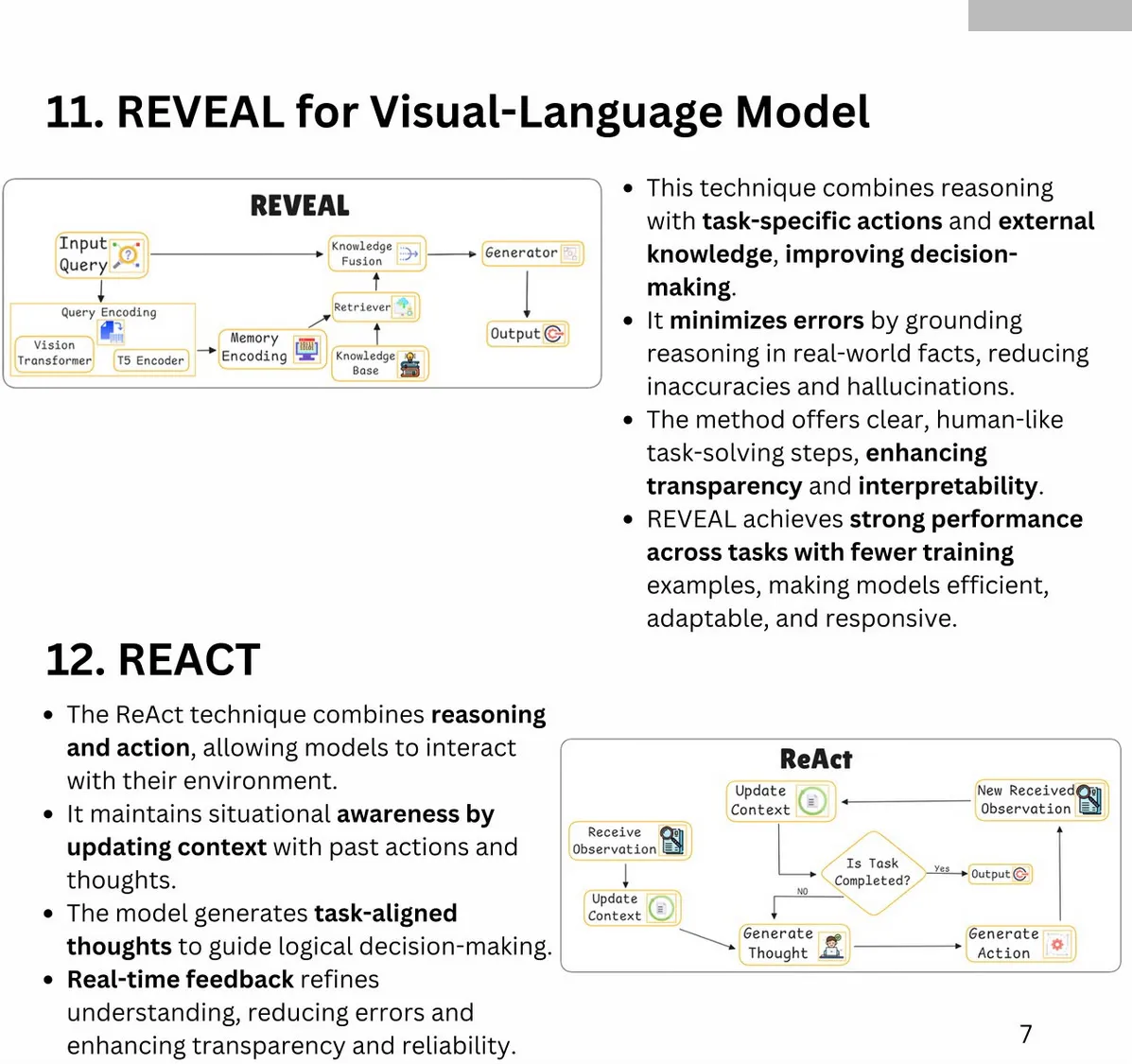
Why Agents Are Stupid & What We Can Do About It
YouTube | tactiq.io transcript
-
Challenges of AI Agents:
- Current agents fail at complex, long-running tasks due to compounding errors and lack of world-model reasoning.
- Memory systems are inadequate; retrieval and reasoning are more critical than data storage.
- Lack of common sense and abstract reasoning leads to cascading task failures.
-
Categories of Problems:
- Big Brain: Issues with long-term planning, strategic thinking, and abstraction.
- Little Brain: Tactical errors in moment-to-moment decision-making.
- Tool Brain: Limitations in precision and interface capabilities, such as navigation or physical manipulation.
-
Improving Agents:
- Use reinforcement learning, scalable data, and generalizable algorithms to build better systems.
- Develop shared memory platforms to distribute knowledge among agent systems.
- Incorporate modular skills (e.g., hot-swappable capabilities for specific tasks).
-
Future Directions:
- Focus on building middleware and improving fine-tuning for task-specific intelligence.
- Advocate for open-source contributions to compete with large-scale labs.
- Aim for better integration of agent intelligence into real-world workflows.
Recommended Resources
- Book: A Brief History of Intelligence19 – Explores neurobiology and AI.
- Dataset/Model: Wave UI Dataset20 – Data for training UI interaction models.
- Model: MOMO by AI221 – Fine-tuned for GUI and robotics accuracy.
Atomic Agents: A Modular Framework for AI Agents
linkedin.com GitHub Repo
Author: Pietro Bolcato22
-
Overview:
- Atomic Agents23 is a framework for building AI agents with a focus on simplicity, modularity, predictability, and control.
- Designed for reliable AI systems and built on top of Instructor with Pydantic for data validation.
-
Key Features:
- Modularity: Combine reusable components to build AI applications.
- Predictability: Clear input and output schemas enhance reliability.
- Extensibility: Easily integrate new components.
- Control: Fine-tune individual system parts.
-
Dynamic Context:
- Uses Context Providers to enhance agent responses with real-time information.
- Allows chaining of agents and tools by aligning their input and output schemas for reusability.
-
Commentary:
- Craig Harper: Praises Atomic Agents as a strong alternative to LangChain.
The Impact of Reducing Work in Progress (WIP)
linkedin.com
Author: Allen Holub
- Core Insight: Limiting WIP to one task maximizes productivity by avoiding multitasking penalties. Each additional task reduces productivity by ~20%.
- Dependency Reduction: Empower cross-functional teams to handle platform/database changes directly while aligning with others via occasional meetings to ensure consistency.
- Mathematical Impact: Working on three 5-day tasks simultaneously extends delivery from 5 days per task to 21 days for all tasks.
- Commentary:
- Dependency-heavy structures (e.g., platform teams) amplify delays and inefficiencies.
- Cross-functional teams with clear boundaries prevent entropy (Ben B.).
- Aligns with “Team Topologies” concepts, focusing on cognitive load and reducing inter-team dependencies (Luiz Armesto).
- “Slow is smooth. Smooth is fast.” philosophy fosters accuracy and smooth workflows (Craig Imlach).
Additional Resources24
⛅🌱 Cloud Seed: Simplifying Cloud Services with GitLab
-
Overview:
- Cloud Seed integrates Google Cloud services directly into GitLab for streamlined cloud adoption and automation.
-
Key Capabilities:
- Google Cloud Service Accounts:
- Generate authentication credentials from the GitLab interface for wide-ranging integrations with Google Cloud.
- Deploy to Google Cloud Run:
- Automate containerized app deployments, including Preview Environments for branch-specific commits.
- Provision Google Cloud SQL Databases:
- One-click provisioning of PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQL Service instances, with Git environment awareness.
- Google Cloud Service Accounts:
-
Use Cases:
- Cloud-native app development with seamless deployment.
- Cloud migration and modernization with automated database provisioning.
-
Positive Business Outcomes by Persona:
- Developers & Engineers: Continuous deployment and easy database provisioning.
- Managers: Preview environments for feature validation.
- Ops Teams: Secure, standardized deployment pipelines.
- Directors: Improved operational efficiency, reduced compliance risk.
Entrepreneurship Concepts: 10 Concepts Every Entrepreneur Should Learn
linkedin.com
Author: Guillermo Flor
- Peter Thiel: Compete by creating something unique. Source
- Naval Ravikant: Guide to wealth creation. Source
- Asymmetric Risks: Leveraging risks effectively. Source
- Startup Cash Management: By Sequoia Capital. Source
- Ben Horowitz: Contribution trumps passion. Source
- Brian Chesky (Airbnb): Funding requires just one “yes.” Source
- Jen-Hsun Huang (Nvidia): Focus on massive action over business plans. Source
- Product Market Fit: Understanding its role. Source
- Sam Altman: Keys to success. Source
- Steve Jobs: Start with customer experience, then innovate backward. Source
Comments
- Dennis Trautmann: Focus on passion, grit, and customer obsession.
- Dr. Amr El Fawal: Criticism of Adam Neumann as a poor example.
- Sharad Agarwal: Differentiates passion (Web2) and obsession (Web3).
- Georgi Furnadzhiev: Adds Alistair Croll’s “just evil enough” concept.
- PRADEEP KUMAR GUPTAA: Balancing uniqueness with market validation.
Resources Captured28293031323334353637:
Pdoc: Auto-Generate API Documentation
linkedin.com
Author: Banias Baabe
Date: 1 month ago
-
Introduction to pdoc:
- A simple library for creating documentation pages aligned with your Python module hierarchy.
- Minimal configuration; runs without the complexity of setting up tools like Sphinx.
-
Comparison with Alternatives:
- Positioned as an easier-to-use alternative to Sphinx.
- Comments mention that
mkdocsoffers more flexibility in themes and styling.
Comments
- Muhammad Bilal Khatri: Prefers
mkdocsfor its flexibility in theming and styling. Questions whetherpdocoffers similar features.
Launch of New RAG Course by Elvis S.
Modules:
- RAG Fundamentals:
- Core components, architecture, and advantages over traditional AI.
- Building Naive RAG:
- Construct a personalized tutor.
- RAG Chat Assistant:
- Build a customer service chatbot with query expansion techniques.
- Advanced RAG:
- Implement advanced techniques like CoT prompting and tool integration.
- Agentic RAG:
- Build an Agent RAG system interacting with tools (calculator, reasoning chain, LLM chain).
- Deploy RAG Apps:
- Create shareable online applications and improve iteratively.
- Course Link40
Vaughn Vernon Workshop: Ports and Adapters Architecture
YouTube Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3
Author: Vaughn Vernon
1. Ports and Adapters Overview
- Simplifies separating business logic (inside) from technical details (outside).
- Ports define application interactions (e.g., catalog queries), while Adapters handle technological concerns (e.g., HTTP or database queries).
- Supports both monolithic and microservice architectures, ensuring technology independence for the domain model and a clear separation of concerns.
2. Core Architecture Concepts
- Driver Side:
- Handles external requests (e.g., HTTP) via adapters like
CatalogController. - Translates incoming requests into actions for the domain model or application services.
- Handles external requests (e.g., HTTP) via adapters like
- Driven Side:
- Manages external dependencies like databases.
- Example:
PostgresCatalogRepositoryimplements aCatalogRepositoryinterface.
- Role-Based Interfaces:
- Differentiate user types (e.g., customers vs. content managers) to enforce security and role-specific access.
- Compiler-level enforcement prevents misuse of role-specific methods.
3. Behavior and Enhancements
- Business Logic:
- Catalog services manage actions like querying categories/products, adding items to carts, and defining products/categories.
- Role-Based Behavior:
- Customers access basic catalog functions.
- Content managers access advanced features for managing categories and products.
- Access Control:
- Implemented through role-based interfaces, adapters, or service layers to handle transactional and security concerns.
4. Dependency Management
- Lightweight alternative to IoC containers:
- Constructor injection simplifies dependency handling.
- Instantiate components in a
mainmethod (e.g.,PostgresCatalogRepository,CatalogService).
- Benefits:
- Removes external dependencies for tests.
- Simplifies architecture without sacrificing flexibility.
5. Testing and Mocking
- Custom mocks for port interfaces ensure fast, technology-independent tests.
- Testing the catalog service and repository independently improves reliability and speed.
6. Naming and Organization
- Modules and Packages:
- In Java:
com.company.application,com.company.model,com.company.infrastructure. - In .NET:
Company.Application,Company.Model,Company.Infrastructure.
- In Java:
- Separation of Concerns:
- Application layer: Contains core business logic and services.
- Infrastructure layer: Adapters handling external dependencies like controllers or database access.
- Domain layer: Represents core entities and aggregates.
7. Benefits
- Technology independence for the domain model.
- Reusable patterns for different interaction types.
- Fast, controlled testing with clear separation between layers.
Additional Resources
- Implementing Domain-Driven Design – Foundational book by Vaughn Vernon.
- Strategic Monoliths and Microservices – Patterns for clean architecture and service design.
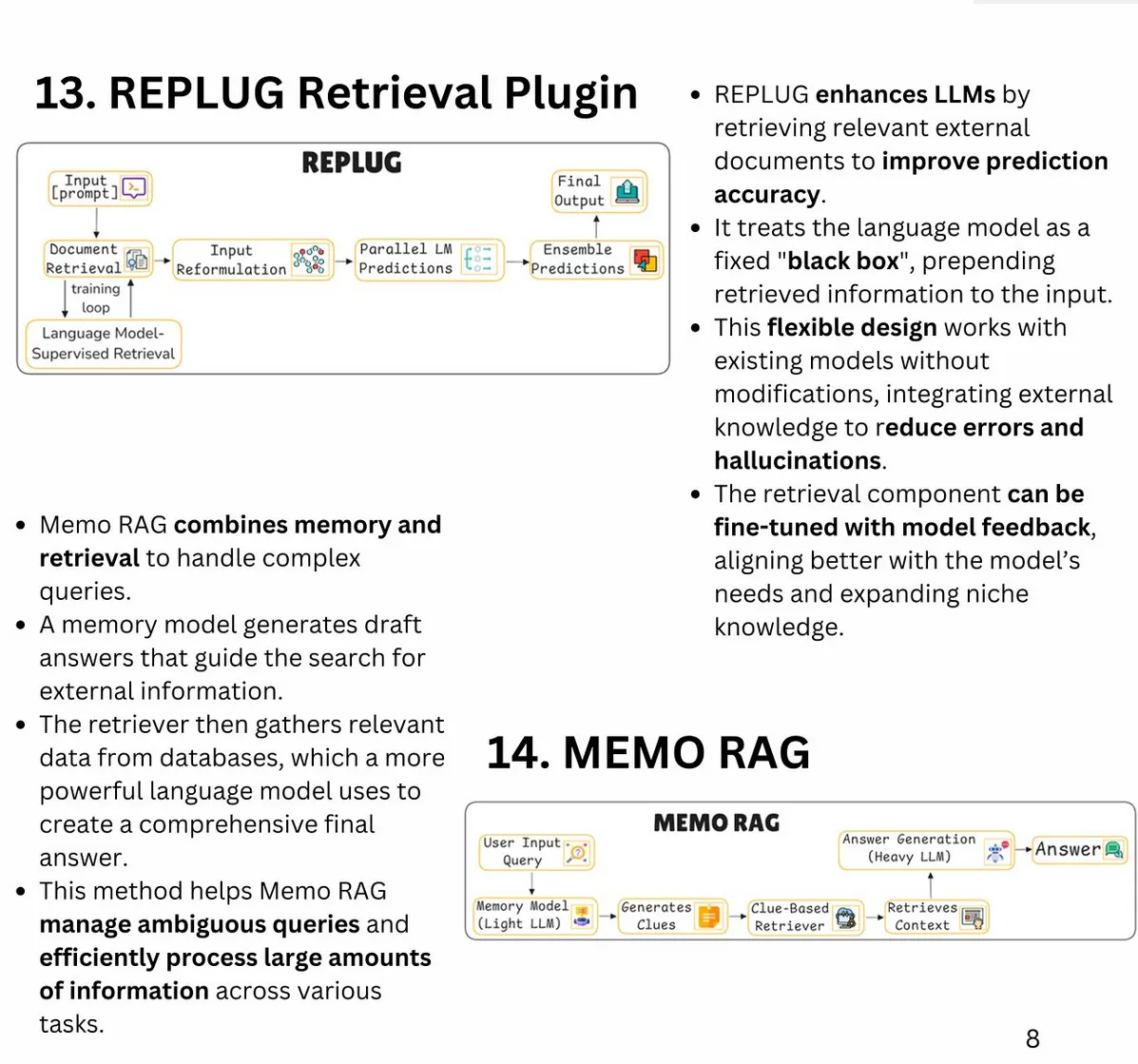
A Systematic Survey of Prompt Engineering in Large Language Models: Techniques and Applications
-
Prompt Engineering Definition: Strategic task-specific instructions guide LLM and VLM outputs without parameter modifications.
-
Core Techniques:
- Zero-Shot Prompting: Leverages pre-existing knowledge without labeled data.
- Few-Shot Prompting: Demonstrates tasks with a few examples to enhance understanding.
- Chain-of-Thought (CoT): Step-by-step reasoning to handle complex logic and problems.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Integrates external knowledge for factually enriched prompts.
- Chain-of-Code (CoC): Uses pseudocode to improve logical and semantic reasoning.
- Emotion Prompting: Enhances LLMs’ emotional intelligence through targeted stimuli.
-
Advanced Methods:
- Graph-of-Thought (GoT): Models reasoning processes as directed graphs for complex tasks.
- System 2 Attention (S2A): Selectively attends to relevant context for enhanced focus.
- Chain-of-Verification (CoVe): Emulates human-like verification processes to improve factual accuracy.
-
Applications:
- Reasoning, hallucination reduction, code generation, user interaction, and intent understanding.
- Notable datasets: GSM8K, TriviaQA, WikiTQ.
Guide to Weisbord’s 6 Box Model
-
Purpose:
- Focuses on business objectives, target markets, and strategic alignment.
- Questions include: Why does the business exist? What are its vision and mission?
-
Structure:
- Reviews organizational design, departmental relationships, and operational efficiency.
- Emphasizes creating structures suited for achieving strategic goals.
-
Relationships:
- Addresses team dynamics, collaboration, communication, and conflict resolution.
- Negative relationships can obstruct strategy execution.
-
Rewards:
- Considers employee incentives, recognition systems, and goal-setting processes.
- Poor reward systems can demotivate staff.
-
Leadership:
- Highlights the role of managerial behavior and alignment with company values.
- Good leadership ensures unified team direction.
-
Helpful Mechanisms:
- Focuses on tools, systems, and processes that support business execution.
- Includes regular system reviews and feedback collection.
Advantages
- Simple and comprehensive framework for internal analysis.
- Broad application across company or department levels.
Disadvantages
- Solely inward-looking; lacks external market consideration.
- Time-consuming to implement thoroughly.
Alternatives
- VRIO Framework: Focuses on competitive advantage.
- VMOST Analysis: Links strategy with business activities.
Hierarchy of Traction for VC Pitches
linkedin.com
Author: David Foreman
- Traction Hierarchy:
- Revenue / ARR: Definitive proof of market success.
- Contracted ARR: Signed agreements for predictable future revenue.
- Paid Proof of Concepts (PoCs): Validates willingness to pay.
- Unpaid PoCs: Demonstrates user interest and product validation.
- Trials: Early user feedback through active engagement.
- Master Service Agreements (MSAs): Framework agreements without guaranteed implementation.
- Letters of Intent (LOIs): Soft commitments showing potential interest.
- Pipeline Value: Early discussions; lowest credibility for traction.
Insights
- Focus investor attention at the highest credible traction level.
- Awards don’t matter unless tied to revenue, market access, or customer acquisition.
- MSAs are often low-value unless they lead to active adoption.
Comments
- Scott Newton: Awards can matter if they provide grants, target customers, or unique market access.
- Jem Stein: Pipeline value often overstated; skepticism warranted.
- Paul Adams: True traction requires monetary transactions; user metrics without revenue are insufficient.
- Metin Emenullahi: Questions the practicality of high-ranking unpaid PoCs in early-stage EU startups.
- Evaldas Girskus: Founders should understand Go-To-Market (GTM) strategies and scale early successes.
- Pete Stubbs: Consider alternative funding, such as founder-friendly capital online.
- Chris Parnell: “R for Revenue, not for awaRds. It’s traction, not trickion, that matters.”
How to Miss Your Dates and Fail Your Goals With Finesse
scarletink.com
Author: Dave Anderson
Date: January 20, 2022
-
Key Principles for Managing Goal Failure:
- Understand the business impact: Assess the consequences of missing a date.
- Minimize harm: Strategize ways to reduce negative effects.
- Reinstate predictability: Ensure the team and business can depend on revised deliverables.
-
Avoid Personal Obsession:
- Focusing on personal reputation may hinder effective decision-making.
- Example: A manager, panicked about optics, proposed rushing a critical fix, risking major customer impact instead of tolerating a minor delay.
-
Critical Questions When Delays Arise:
- Why was the original date set? Often arbitrary and outdated.
- What is the actual business impact of the delay? Typically less severe than perceived.
- What are the risks of rushing? Hasty fixes often introduce greater long-term harm.
-
Takeaway: Success isn’t about avoiding failure but thoughtfully managing it.
Model2Vec: Efficient Static Embeddings
-
Overview:
- Optimizes Sentence Transformers into compact static embeddings, 15x smaller and up to 500x faster.
- Ideal for NLP tasks like classification, clustering, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
-
Key Features:
- High Performance: Outperforms static models like GLoVe with minimal trade-offs.
- Fast Distillation: Distill models in ~30 seconds on a CPU without training data.
- Lightweight: Minimal dependencies; small models (e.g.,
potion-base-8Mat 30MB). - Seamless Integration: Supports HuggingFace, Sentence Transformers, and txtai.
-
Example Code:
from model2vec import StaticModelmodel = StaticModel.from_pretrained("minishlab/potion-base-8M")embeddings = model.encode(["Example sentence 1", "Example sentence 2"])
Kubernetes Troubleshooting Use Cases
linkedin.com Author: Govardhana Miriyala Kannaiah Date: 4 weeks ago
-
Key Troubleshooting Use Cases:
- Fixing Kubernetes Node Not Ready: Guide here.
- Resolving Kubernetes Node Disk Pressure: Guide here.
- Understanding CreateContainerError: Guide here.
- Understanding CreateContainerConfigError: Guide here.
- Explaining Kubernetes ImagePullBackOff: Guide here.
- Explaining Kubernetes RunContainerError: Guide here.
- Fixing OOMKilled Issues: Guide here.
-
Newsletter: Bite-sized TechOps examples covering DevSecOps, Cloud, Containerization, IaC, GitOps, and MLOps. Subscribe here.
-
Twitter (X): Follow Govardhana on X for updates here.
Adaptive RAG for Optimized Query Handling
linkedin.com
LangGraph Adaptive RAG Tutorial
- Adaptive Retrieval: Dynamically selects the optimal strategy for handling queries based on complexity, improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Complex Queries: Uses iterative multi-step retrieval for layered, accurate responses.
- Moderate Queries: Employs single-step retrieval for concise and relevant information.
- Simple Queries: Skips retrieval entirely, generating direct answers.
- Efficiency: Minimizes unnecessary compute usage, offering substantial cost savings at scale.
- Implementation: Built with LangGraph, leveraging LangChain for a modular, easy-to-extend pipeline.
Example Workflow
- Query complexity predicted using a lightweight model.
- Framework dynamically selects between iterative, single-step, or direct answer retrieval methods.
- Adaptive execution ensures cost and compute efficiency.

Resources and Tools
- LangGraph Adaptive RAG Tutorial: Step-by-step guide to implementing the Adaptive RAG pipeline.
AWS Card Clash: Game-Based Learning for Cloud Architecture
-
Overview:
- A 3D virtual card game to explore and learn AWS Cloud architecture.
- Designed for both beginners and experienced users to enhance AWS knowledge.
-
Key Features:
- Play to Learn: Experiment with AWS Cloud service cards to optimize designs and win through friendly competition.
- Architectural Insights: Identify and deploy scalable, efficient AWS solution architectures.
- Game Mechanics: Use strategy cards to defend solutions or disrupt opponents’ deployments.
- Practical Learning: Explore real-world AWS service applications via interactive 3D gameplay.
-
Benefits:
- Develop foundational knowledge of AWS Cloud services and interfaces.
- Enhance understanding of scalable, efficient cloud solution designs.
- Combine learning with engaging, competitive gameplay.
-
Availability:
- Accessible through all versions of AWS Skill Builder.
Perform Outlier Detection More Effectively Using Subsets of Features
towardsdatascience.com
Author: W Brett Kennedy
Date: November 24, 2024
- Challenges of Outlier Detection: Curse of dimensionality affects high-dimensional data; relevant subspaces improve detection accuracy.
- Subspaces: Identify subsets of features to isolate anomalies; mitigates noise from irrelevant features, enhances interpretability, and reduces computation.
- Key Algorithms:
- KNN & LOF: Detect anomalies using local and global neighborhood distances.
- SOD: Leverages shared nearest neighbors for robust subspace detection.
- FeatureBagging: Randomly creates feature subsets; ensembles base detectors like LOF.
- Advantages of Subspaces:
- Improved interpretability and scalability.
- Parallel execution and reduced dimensionality effects.
- Easier model tuning over time.
The Essence of Executive Presence
linkedin.com
Author: Ethan Evans
-
Definition of Executive Presence:
- 60% gravitas (confidence, decisiveness under pressure).
- 30% communication (speaking, reading rooms, holding attention).
- 10% appearance (grooming and professionalism, critical for first impressions).
-
Strategies for Improvement:
- Practice public speaking in safe settings (e.g., Toastmasters).
- Build emotional intelligence through meditation and reflection.
- Seek feedback on room-reading and communication post-meetings.
- Use structured influence techniques (e.g., How to Win Friends and Influence People).
- Consider professional stylists for appearance refinement.
-
Key Comments:
- Mala Munisamy: Balancing executive presence with authentic, empathetic leadership is challenging.
- Maria Shum: Thoughtfulness and insights over loudness; empathy aids in emotional management.
- Joseph Feduccia: Focus on effective leadership first, leveraging situational awareness and mentoring.
- Sue Bethanis: Establish common ground to ease conversations and build likability.
- Sasa Djolic: Highlights risks of “dark patterns” in executive presence conflicting with DEI values.
- Adrian Neumeyer: Emotional control is central to leadership presence.
-
Resources Mentioned:
- How to Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie.
- Cialdini’s principles of influence.
- Ethan’s course, Breaking Through To Executive (Maven Platform).
21 Rules for Operating Software at Scale
linkedin.com
Author: Owain Lewis
Owain’s Post:
- Know if things break before users do.
- When things break, ask: “What changed recently?”
- Stale runbooks are dangerous. Update them.
- Dashboards should answer: “Is everything OK?”.
- Failures are inevitable. Prepare for the worst.
- Practice rollbacks before you need to rollback.
- Regularly practice disaster recovery.
- Backups are non-negotiable. Automate them.
- Every page should need some action.
- Use error budgets to balance reliability and innovation.
- Build a blameless culture that learns from failure.
- Make fixing things “one-click” where possible.
- Feature flags decouple deployment from release.
- Roll out changes progressively.
- Testing environments aren’t optional.
- Load test systems to uncover weak points.
- Simplicity scales. Design for maintainability.
- Toil reduction improves morale.
- Avoid 24/7 on-call where possible.
- Practice breaking things to build resilience.
- Have clear SLOs and SLAs.
Comments:
- Automation and Monitoring: Automate repetitive tasks, establish monitoring systems to detect issues early, and regularly tune performance. (Haroon Mushtaq)
- Blameless Culture: Continuous learning from failure and avoiding blame is crucial for building trust and process improvement. (Gregor Ojstersek, Elis Wilkins)
- Rollback Preparedness: Practicing rollbacks has proven invaluable in many cases. (Eitan Yehoshua)
- Simplicity and Failure Planning: Systems at scale require prioritizing simplicity and preparing for failure to handle complexity. (Mike Leber)
- Key Takeaways: Automation, resilience, and simplicity stand out as themes among the rules and comments.
AWS Systems Manager Features
-
Secure alternative to bastion servers and direct SSH access
-
Unified Node Management:
- Manage EC2 instances, hybrid servers, or multicloud nodes via a unified interface.
- Comprehensive visibility of managed and unmanaged nodes across AWS accounts and Regions.
- Gain detailed node insights: instance ID, OS details, installed agents, and tags.
-
Patching and Compliance:
- Automate OS and software patching across cloud and on-premises environments.
- Use patch baselines to auto-approve updates, override rules, and schedule maintenance windows.
- Ensure patch compliance and seamless updates.
-
Task Automation:
- Secure remote management eliminates bastion hosts, SSH, and remote PowerShell.
- Automate tasks like registry edits, user management, and software installations.
-
Simplified Node Diagnostics:
- Detect and remediate SSM Agent issues, including misconfigurations and outdated software, using predefined runbooks.
-
Amazon Q Developer:
- Extend visibility using natural language querying for node data across AWS accounts and Regions.
- Quickly identify and act on issues with AI-enhanced insights.
Frustrations with Local AWS Lambda Development
-
Main Issues with Local Lambda Development:
- hyun88: AWS lacks user-friendly local development tools for Lambda.
- unpluggedcord: Advocates using
makecommands to invoke Lambdas directly, simplifying the setup.
-
Alternative Solutions:
- Redis vs. DDB:
- Naher93: Suggests switching from Redis to DynamoDB (DDB) to reduce costs (~$20–$30/month as a dealbreaker).
- Lambda Live Debugger:
- Background_Bag2770: Promotes Lambda Live Debugger for cost-free, serverless infrastructure debugging.
- Features:
- Compatible with various frameworks (CDK, SLS, SAM, Terraform).
- Minimal setup required (e.g., profile and region configuration).
- Supports production debugging with Observability mode.
- Redis vs. DDB:
-
Recommendations for Common Triggers:
- Use AWS’s built-in invoke functionality for triggers like SQS.
Relevant Tool:
Describe Your Ticket Workflow
-
Flexible Approaches:
- Retrospectives are essential for optimizing workflows (multiple commenters).
- Experimentation and iteration are key; no single “standard” applies universally.
-
Ownership and Accountability:
- Epics often created by leadership or Product Owners; tasks by developers for technical details (Charming_Complex_538, iwek7).
- Developers involved in ticket creation and estimation to improve accountability (Charming_Complex_538).
-
Scope Management:
- Scope defined through negotiation between PMs (business value), EMs (time-to-market), and ICs (feasibility) (Charming_Complex_538).
- Adjustments handled collaboratively; PMs usually manage rescoping with input from developers (iwek7).
-
Separate Bug Tracking:
- Some teams use separate ticket systems for bugs to streamline workflows (Informal-Dot804).
-
Challenges and Anecdotes:
- Misalignment between business and dev teams leads to last-minute prioritization issues (HowTheStoryEnds).
- “FrAGILE” methodologies can result in poor developer outcomes when misapplied (Fluid_Frosting_8950).
-
Document retro action items and track progress (Charming_Complex_538).
-
Keep workflows elastic; adapt based on team needs (iwek7).
-
Avoid rigid processes; focus on solving problems practically (discondition).
Saplings: A Framework for Search-Enabled AI Agents
GitHub
Author: Jonathan Shobrook
- Plug-and-play Search Algorithms: Implements Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), A*, and Greedy Best-First Search for AI agents.
- Integration with OpenAI APIs: Leverages OpenAI function calling for reasoning and task execution.
- Modular Design:
- Agents: MonteCarloAgent, AStarAgent, GreedyAgent, and baseline COTAgent.
- Tools: Customizable utilities for specific tasks (e.g., arithmetic, web navigation).
- Evaluator: Guides search with LLM-scored trajectories.
- Advanced Tooling:
- Tools access agent memory for dynamic task handling.
- Output reformatting for model presentation.
- Terminal tools enforce trajectory finalization.

Serverless.tf: Serverless Application Management Using Terraform
Overview
- What is it: Opinionated open-source framework for serverless application and infrastructure lifecycle management on AWS using Terraform.
- Key Value: Simplifies the complexity of serverless workflows by consolidating tools into a Terraform-based ecosystem.
- Core Benefits:
- Unified infrastructure management for all resources, reducing fragmentation.
- Reusable, high-quality components using Terraform AWS modules.
- Supports faster lifecycle management and accurate AWS service interactions.
How it Differs
- Single-Tool Approach: Replaces multiple tools (e.g., Serverless Framework, AWS CLI, Makefiles) with Terraform.
- Reusable Components: Built on years of development with Terraform AWS modules, avoiding custom plugin code in JavaScript.
- Environment Management: Enables spinning up complete environments for testing/development with real AWS services.
Supported AWS Services
- Lambda, AppSync, EventBridge, Step Functions, API Gateway, DynamoDB, Aurora Serverless, RDS Proxy, S3, SNS, SQS, CloudFront, CloudWatch, and more.
- Latest additions: AWS SSM Parameter Store, AWS Secrets Manager.
FAQ Highlights
- Platform: AWS-only.
- Runtimes: All supported without restriction.
- Workflow: CI/CD customizable, managed as code.
- Support: Commercial support available from Betajob.
Resources
- GitHub Repository – Terraform AWS modules.
- AWS Serverless Services – Official AWS serverless homepage.
- Examples of Terraform AWS Modules – Practical use cases and integration examples.
Free Submission to 30 Directories for SaaS or AI Tools
reddit.com
Author: Revolutionary_Hair73
-
Service Overview:
- Revolutionary_Hair73 offers free manual submission of SaaS/AI tools to 30 directories with at least 50k monthly traffic.
- The aim is to provide SEO backlinks to boost Domain Rating (DR).
- Service offered in exchange for testimonials during its early phase.
-
Key Features:
- 30 high-quality backlinks to improve SEO.
- Weekly progress reports shared with participants.
- Designed to save founders time and effort in early-stage marketing.
-
Planned Development:
- The service is currently manual but may evolve into an automated solution with paid tiers.
-
Critiques and Feedback:
- fanandrew: Warns that many directories have minimal SEO impact due to high outgoing link counts.
- inglandation: Questions potential for paid tiers and service scalability.
- JoaoRochaOnReddit: Inquires about niche-specific directories for unique tools like a real estate buying assistant.
-
Links and Resources:
- Service Website: LinkPath
Comments highlight varying opinions on directory submission effectiveness, with some skepticism about its long-term SEO impact.
The Accidental CIO: A Lean and Agile Playbook for IT Leaders
amazon.com
Author: Scott Millett
- Core Focus: Balancing innovation and operational stability using lean, agile, and design thinking frameworks.
- Key Frameworks:
- Cynefin for decision-making.
- Wardley Mapping for strategy alignment.
- Team Topologies for organizational design.
- Holacratic and hierarchical structures combined for adaptability.
- Content Breakdown:
- New Systems of Work: Philosophies like agile and systems thinking to inspire teams.
- Adaptive Operating Models: Governance, talent management, and structural components for dynamic contexts.
- Strategy to Execution: From business architecture to IT strategy deployment.
- Practical Tools: Emphasis on actionable advice, case studies, and clear diagrams for real-world IT leadership.
- Insights: Explores the CIO’s paradox of fostering innovation while ensuring operational reliability.
The Career-Changing Art of Reading the Docs
pluralsight.com
Author: Forrest Brazeal
Date: June 8, 2023
- Key Strategy: Read documentation for one job-relevant technology, cover-to-cover, weekly. Focus on technologies you actively use.
- Approach:
- Read docs strategically to build a holistic mental model, not tactically for specific problems.
- Actively question and review understanding; reread regularly to reinforce knowledge.
- When docs are inadequate, read source code for deeper insights.
- Common Objections Addressed:
- Lack of memory: Focus on technologies with immediate relevance and context.
- Lack of time: Dedicate daily blocks, even 30 minutes, for consistent progress.
- Poor documentation: Apply common sense, or rely on code for OSS projects.
- Outcomes:
- Build rare, authoritative expertise in your technical niche.
- Enhance troubleshooting by connecting disparate knowledge.
- Enable career growth through demonstrated mastery.
- Example: Jared Short reads AWS service docs weekly, gaining insights that resolve complex issues and elevate his reputation.
Critique of Timeboxing in Scrum and Alternatives
linkedin.com
Author: Allen Holub
-
Holub’s Perspective:
- Timeboxing (e.g., Sprints) creates unnecessary overhead, detracting from actual work.
- Advocates for small, focused stories without artificial deadlines, emphasizing collaboration and workplace pride.
- Suggests adding slack time for learning and reflection instead of rigid timelines.
- Don’t subdivide into tasks. Instead, narrow scope to the point where there are no variables or decisions. Every one of those narrowings is a separate story.
-
Proponents of Timeboxing:
- Gene G.: Timeboxing fosters discipline, aligns cross-team collaboration, and mitigates estimation risks.
- Ludovic Urbain: Properly implemented ceremonies like sprint planning/review optimize workflow and reflection without becoming bottlenecks.
-
Criticism of Timeboxing:
- Igor Zhavrid: Argues for Kanban over Scrum for flexibility, focusing on high-level initiative planning and reducing waste in sprint planning.
- James Ritzman: Compares software estimates to construction projects—uncertainty and dynamic changes make rigid commitments unrealistic.
Additional Insights
- Scrum’s Practicality: Debates highlight inefficiencies in large organizations and challenges with scaling across teams.
- Kanban as an Alternative: Promoted for continuous flow, adaptability, and reduced meeting overhead.
- Cultural Aspect: Creating a disciplined yet flexible environment is seen as more effective than adhering to rigid frameworks.
Dexie.js: A Minimalistic Wrapper for IndexedDB
-
Overview:
- Lightweight wrapper for IndexedDB (~29k minified and gzipped).
- Focused on simplicity, reactive capabilities, and ease of learning.
-
Key Features:
- Reactive Queries: Real-time database mirroring with integration in frameworks like React, Svelte, Vue, and Angular.
- Concise API: Simplifies IndexedDB operations with straightforward syntax.
- Syncing Made Simple: Dexie Cloud enables local-first apps with authentication and access control.
-
Framework Examples:
- React:
useLiveQueryfor real-time DB queries in components. - Svelte:
liveQueryfor observable DB queries in templates. - Vue: Uses
liveQuerywithuseObservablefrom@vueuse/rxjs. - Angular:
liveQuerywith async pipes for reactive data.
- React:
-
Sync Implementation:
- Create a cloud database:
npx dexie-cloud create - Whitelist app origins:
npx dexie-cloud whitelist http://localhost:3000 - Install dependencies:
npm install dexie@latest dexie-cloud-addon - Configure DB with Dexie Cloud.
- Create a cloud database:
The Fantastic Four of System Design (Expanded)
linkedin.com
Author: Alex Xu
Original Fantastic Four
- Scalability: Handles increased load without compromising performance.
- Availability: Ensures minimal downtime and continuous user access.
- Reliability: Delivers consistent and correct results over time.
- Performance: Operates efficiently under peak load with available resources.
Additional Pillars Proposed by Commenters
- Security: Protects against unauthorized access with encryption, authentication (e.g., OAuth), and audits.
- Maintainability: Eases updates/debugging through modularity, clean code, and documentation.
- Cost Efficiency: Minimizes costs using strategies like auto-scaling and serverless architecture.
- Fault Tolerance: Maintains functionality during failures using redundancy, retries, and circuit breakers.
- Observability: Tracks system health via logging, metrics, and tools like Prometheus or Grafana.
- Extensibility: Facilitates future features with microservices and API-first designs.
Key Insights
- Balancing these pillars often requires trade-offs tailored to project needs.
- Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and structured logging aid observability and proactive issue resolution.
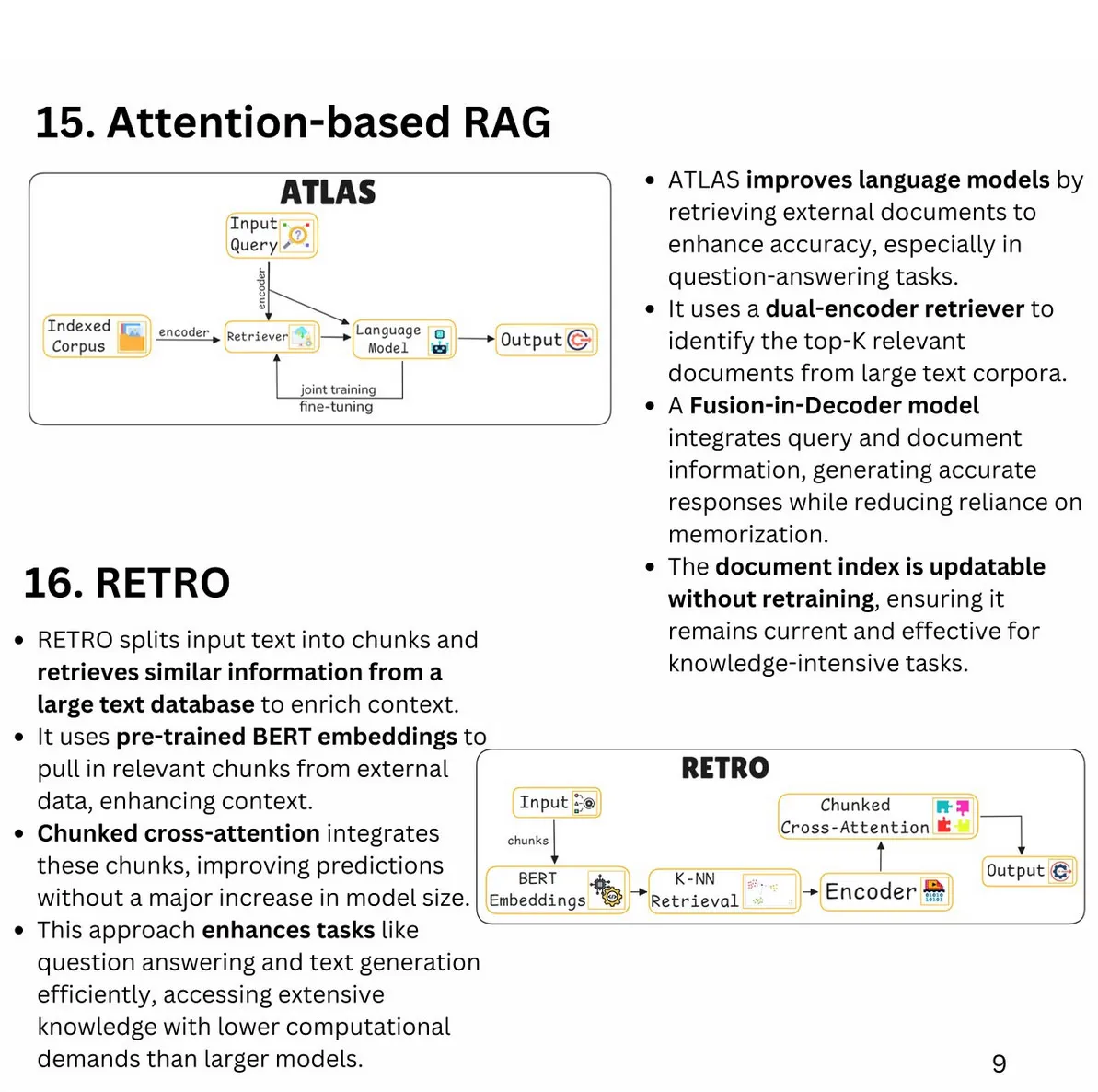
Understanding RAG Architectures: From Naive to Graph Approaches
linkedin.com
Author: Pavan Belagatti
-
Naive RAG:
- Basic implementation with document collection, chunking, dense embedding, and vector search.
- Focus: Simplicity and basic vector similarity.
-
Advanced RAG:
- Enhances Naive RAG with smart chunking, hybrid embedding, re-ranking, and query expansion.
- Focus: Semantic chunking and improved relevance.
-
Multi-modal RAG:
- Handles mixed media types with cross-modal embedding, multi-modal fusion, and modal-specific ranking.
- Focus: Comprehensive understanding of diverse content formats.
-
Graph RAG:
- Uses entity extraction, graph construction, embedding, and traversal for relationship-centric knowledge structures.
- Focus: Complex query reasoning via knowledge graphs.
Resources
- Beginner’s guide to RAG: Read more
- Multi-modal RAG applications: Complete article
- Building multi-modal RAG with LlamaIndex: Explore here
- Video on Agentic RAG: Watch here

PGlite: Postgres Anywhere
-
What is PGlite:
- Lightweight Postgres in WASM, packaged as a TypeScript/JavaScript client library.
- Runs in the browser, Node.js, or Bun without dependencies.
- Supports persistence via IndexedDB (browser) or filesystem (Node/Bun).
- Compact Size: Under 3MB gzipped.
- Includes support for Postgres extensions like
pgvector.
-
Key Features:
- Embedded Database: Works as in-memory or persistent DB.
- Edge-Ready: Sync subsets of server-side Postgres, ideal for AI and RAG workflows.
- Lightweight & Fast: Perfect for unit/CI testing or local/remote development.
- Multi-tab Support: Share a PGlite instance across browser tabs.
- Live Queries: Reactivity for UI updates on DB changes.
The 30 Life-Changing Books Everyone Must Read (According to Naval Ravikant)
productmarketfit.tech
Author: Guillermo Flor
Date: November 26, 2024
-
Naval’s Rule for Reading: Invest freely in books; abandon guilt-free if it doesn’t resonate.
-
Where to Start: “Sapiens” (context on humanity) or “Meditations” (personal guidance).
-
Non-Fiction Recommendations:
- Sapiens by Yuval Noah Harari: Frameworks changing worldview.
- Skin in the Game by Nassim Taleb: Real-world risk-taking insights.
- Poor Charlie’s Almanack by Charlie Munger: Wisdom on rational thinking.
-
Philosophy & Spirituality:
- Meditations by Marcus Aurelius: Naval’s favorite for stoic living.
- The Book of Life by Jiddu Krishnamurti: Profound guide to self-awareness.
- The Tao of Seneca by Seneca: Naval’s go-to audiobook.
-
Science Fiction:
- Ficciones by Jorge Luis Borges: Stories challenging reality perception.
- Snow Crash by Neal Stephenson: Visionary look at tech and societal change.
-
Top Blogs:
- Melting Asphalt (Kevin Simler): Philosophy and psychology.
- Farnam Street (Shane Parrish): Mental models and decision-making.
- Stratechery (Ben Thompson): Tech and business strategy.
-
Additional Resources:
- “How to Get to Product Market Fit” guide.
- 50+ Pitch Decks from successful startups.
- Data Room Template VCs Love49.
Strategies for Managing AWS Costs
linkedin.com
Author: Sandip Das
Key Discussion Points
- Identify High Costs: Use AWS Cost Explorer to pinpoint services driving costs—e.g., Compute, Database, and Data Transfer, especially inter-AZ transfer fees.
- Cost Optimization Suggestions:
- Adopt Savings Plans/Reserved Instances for consistent workloads.
- Replace old instance types with next-gen, cost-efficient alternatives (e.g., t2 → t3).
- Use Spot Instances for non-critical workloads to reduce costs.
- Implement Private Endpoints to minimize data transfer fees.
- Data Transfer Costs: Consolidate services in a single AZ, leverage VPC endpoints, or explore external storage services for cost efficiency.
- Backup Management: Optimize storage policies (e.g., S3 Intelligent-Tiering) to reduce long-term costs.
- Additional Tools:
- AWS Auto Scaling: Adjust instance counts dynamically based on demand.
- Cost Allocation Tags: Attribute costs by team or project for targeted reductions.
- Cost Anomaly Detection: Monitor and address budget overruns.
Comments and Suggestions from Experts
- Nick Jordhan: Focus on instance rightsizing, data transfer optimization (e.g., AWS Direct Connect), and automated scaling.
- Vishal Bulbule: Break down costs by region and tag; enable Savings Plan recommendations via AWS Cost Explorer.
- Manoj K: Optimize AZ synchronization frequency for DB clusters to reduce inter-AZ transfer fees.
- Soumyadip Chatterjee: Replace batch instances with Lambda, use Snowball Edge for large data transfers, and enable RDS performance insights.
Notable Quotes
- “Treat questions as the real answers.” – Sandip Das
- “Outbound data transfers are often the most expensive yet hardest to optimize.” – Manoj K
- “Cost optimization is complicated but achievable with expertise.” – Mohammed Aseem Akram
Automated-AI-Web-Researcher-Ollama: Transforming LLMs into Automated Researchers
Overview
- Purpose: Automates research by breaking queries into focus areas, conducting web searches, scraping relevant content, and compiling findings into a structured document.
- Core Workflow:
- Query broken into prioritized focus areas.
- Web searches and scrapes content.
- Documents results, including source URLs.
- Self-improving search cycles for deeper insights.
- Generates comprehensive summaries and enables Q&A.
Key Features
- Automated research planning with prioritized focus areas.
- Systematic web search, scraping, and documentation.
- Research summaries and post-research Q&A.
- Self-improving search mechanisms.
- Configurable LLM settings (Ollama-based).
ZenML LLMOps Database Overview
-
Purpose: A curated database of 372 real-world LLMOps implementations.
- Provides detailed summaries and technical notes for various use cases.
- Filters available by tags like
amazon_aws,prompt_engineering,rag,scalability, and more.
-
Highlighted Use Cases:
- Multilingual Document Processing: Human-in-the-loop pipelines for structured outputs, regulatory compliance, and translation workflows.
- HR/Payroll Generative AI Platform (ADP): Focus on fine-tuning, scalability, and compliance in high-stakes environments.
- RAG Systems Optimization (AWS GenAIIC): Lessons on chunking, semantic search, and scaling production-grade RAG architectures.
- Manufacturing AI Implementation (Accenture): Multi-use case study covering IoT, orchestration, and fallback strategies in compliance-heavy industries.
-
Technical Tags:
- Covers tools, techniques, and concerns such as
vector_search,fine_tuning,multi_modality,monitoring, andlegacy_system_integration.
- Covers tools, techniques, and concerns such as
Resources Captured50:
Node.js v22.12.0 LTS Release
nodejs.org
Author: Ruy Adorno
Date: December 3, 2024
- Key Feature: Enables
require(esm)by default.- Simplifies compatibility between CommonJS (CJS) and ECMAScript Modules (ESM).
- Impact on Ecosystem:
- KaBanks: Concerned this may slow the transition to ESM as CJS now “just works” with ESM.
- Ryan Shaul: Views this as a major step toward ESM-only libraries, reducing the need for dual publishing.
- Vincent: Highlights reduced overhead for library maintainers, easing the shift toward ESM.
Relevant Links:
Incident.io: Unified Incident Management
- Integrated Incident Management:
- Combine on-call scheduling, incident response, and status pages in one platform.
- Automated workflows in Slack and Teams ensure consistent responses.
- Alert Integration:
- Centralize alerts from multiple sources for seamless incident creation and escalation.
- Customer Communication:
- Real-time updates through public, private, and internal status pages.
- Team Coordination:
- Scheduling, escalation paths, and mobile app to ensure 24/7 readiness.
- Post-Incident Insights:
- AI-powered insights and analytics to prevent incident recurrence.
Predicting the Future of Distributed Systems
blog.colinbreck.com
Author: Colin Breck
Date: August 25, 2024
-
Object Storage Trends:
- Becoming the backbone for transactional and analytical systems due to reliability, flexibility, and two-way-door decisions.
- Expanding features: cross-region replication, immutability, tiered storage, and interoperability (e.g., S3-compatible APIs).
- Tools like Parquet, Delta Lake, and DuckDB facilitate seamless data integration and processing.
-
Programming Models:
- Emerging platforms (Kalix, Dapr, Temporal, wasmCloud, etc.) abstract distributed system complexities (state, workflows, and failures).
- WebAssembly offers portability and security, potentially enabling migration paths and multi-environment workloads.
- Long-term trends: infrastructure handles more auxiliary logic (e.g., HTTP servers, logging), leaving “business logic” as portable and secure.
-
Decision Framework:
- One-Way-Door Decisions: Final, high-risk technology choices (e.g., programming models).
- Two-Way-Door Decisions: Flexible investments (e.g., object storage) promote iterative innovation.
-
Macro Observations:
- Distributed systems will prioritize modularity, separation of concerns, and ease of scaling.
- Early adopters may gain competitive advantage; broader industry adoption depends on clarity and maturity of new paradigms.
Kubernetes Interview Questions and Resources
linkedin.com
Author: Ranjan Yadav
- What is Kubernetes, and why is it used?
- Explain the components of the Kubernetes master and worker nodes.
- What are Pods in Kubernetes?
- What is the difference between a Pod and a Node?
- What is a Namespace, and why is it used?
- How does Kubernetes handle Pod failures?
- What are the different types of workloads in Kubernetes?
- How does a Deployment work?
- What is a StatefulSet, and when would you use it?
- Explain DaemonSets and provide a use case for them.
- What is the difference between ReplicationController, ReplicaSet, and Deployment?
- What is a Service in Kubernetes, and what are the different types?
- How does Kubernetes manage internal and external networking?
- What is a ClusterIP, NodePort, and LoadBalancer Service?
- Explain Ingress in Kubernetes and its use case.
- How does DNS work within a Kubernetes cluster?
- What are Persistent Volumes (PVs) and Persistent Volume Claims (PVCs)?
- Explain the process of binding a PV to a PVC.
- What is a StorageClass, and how does it relate to dynamic provisioning?
- How are ConfigMaps used in Kubernetes?
- What is the difference between ConfigMaps and Secrets?
- How can you securely manage secrets in Kubernetes?
- How do you scale Pods in Kubernetes?
- What is the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA), and how does it work?
- How does Cluster Autoscaler differ from HPA?
- What is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in Kubernetes?
- Explain the difference between Role and ClusterRole.
- What is a ServiceAccount, and why would you use it?
- How can you implement network policies for Pod communication?
- How do you monitor Kubernetes clusters?
- What tools would you use to monitor and log Kubernetes applications?
- What is node affinity?
- What is StaticPods?
- What is Taint and Toleration?
- What is Sidecar Containers and their purpose?
- How to debug specific container logs? Consider there are 2 containers running inside a single pod?
- What are the different deployment strategies in Kubernetes?
- Describe the process of rolling update in Kubernetes?
Building Bluesky: Real-World Engineering Challenges
pragmaticengineer.com
Author: Gergely Orosz and Elin Nilsson
Date: April 23, 2024
- Decentralized Social Network: Bluesky enables user-run servers and full data ownership, distinguishing it from centralized platforms.
- Development Milestones:
- Built by 2 engineers initially; expanded to 15, supporting 25M users.
- Transitioned from experimentation (Postgres, AWS) to scalable federation (ScyllaDB, SQLite, on-prem infra).
- Architectural Evolution:
- v1: Monolithic Postgres + AWS; v2: Modularized, federated architecture with services like Appview and Ozone.
- SQLite for PDS; ScyllaDB for read-heavy services. Federation tested via sandboxes and internal servers.
- Challenges and Lessons:
- Frequent scaling bottlenecks (e.g., Postgres locks); resolved with ScyllaDB.
- Rapid feature builds driven by user feedback (e.g., blocking in one day).
- Transitioned to cost-efficient on-prem hardware for scalability.
- Cultural Insights:
- Open-source ethos; active GitHub and real-time user support via the app.
- Federation shifts moderation and algorithmic control to users.
27 People to Follow for MLOps Insights
linkedin.com
Author: Raphaël Hoogvliets
MLOps architects & executives
- Alejandro Saucedo - OG in MLOps content, amazing newsletter
- Andy McMahon - book author, community organiser
- Aurimas Griciūnas - top notch architectures, system design, posts, blogs
MLOps tech leads
- Eric Riddoch - one of the best I know, shares thought processes
- Maria Vechtomova - true expert, Databricks Beacon
- Matthew Sharp - always looking to question important stuff
- Maxime Labonne - really knows his stuff, wrote multiple books
- Médéric HURIER - insanely great code + docs
- Nemanja Radojkovic - very knowledgeable, has dad jokes
ML engineers
- Başak Tuğçe Eskili - amazing skills, listen up when she speaks!
- Chris B. - doing many interesting projects
- Lisa Becker - multi talented course maker, teacher, and specialist
- Luca Baggi - has a lot of great takes
- Pau Labarta Bajo - MLOps posts, videos, and blogs for learners
- Tales M. - MLOps posts in English and Portugese
LLMOps specialists
- Abi Aryan ☯︎𓁿 - pioneering this subject, book author
- Paul Iusztin - GOAT of LLMOps & MLOps content
- Rafael V. Pierre, MSc. - working with GenAI, LLM, and MLOps
Model monitoring specialists
- Hakim Elakhrass - hilarious and insightful content
- Wojtek Kuberski - CTO at NannyML
- Wiljan Cools - post-deployment data science specialist
- Santiago Viquez - wrote The Little Book of ML Metrics
Community gurus
- Alexey Grigorev - Founder and organiser DataTalksClub
- David Scharbach - Founder and organiser MLOps World conference
- Demetrios Brinkmann - Chief Happiness Engineer MLOps Community
- Meri Nova - Founder and organiser Break Into Data
Product people
- Eduardo Bonet - Product Manager MLOps @ GitLab
- Chris “The Wiz” Alexiuk - Developer Advocate @ NVIDIA
Footnotes
-
RAGFlow GitHub Repository – Workflow and citation-focused RAG framework. ↩
-
Cognita GitHub Repository – Modular RAG with no-code UI and incremental indexing. ↩
-
STORM by Stanford GitHub Repository – Framework for creating Wikipedia-like articles. ↩
-
FlashRAG GitHub Repository – Python toolkit for RAG benchmarking. ↩
-
LLM-App GitHub Repository – Scalable RAG application framework. ↩
-
R2R GitHub Repository – Experimentation-to-deployment RAG framework. ↩
-
PostgreSQL and pgvector for RAG – Simplified RAG pipeline guide. ↩
-
GraphRAG by Microsoft GitHub Repository – Graph-based RAG system. ↩
-
Multi-Modal RAG Chatbot GitHub Repository – Multi-modal RAG architecture for visual Q&A. ↩
-
A Brief History of Intelligence – Neurobiology and AI. ↩
-
Wave UI Dataset – Data for GUI interactions. ↩
-
MOMO by AI2 – Advanced fine-tuned model for GUIs and robotics. ↩
-
Team Topologies – Framework for reducing dependencies and managing team cognitive load. ↩ ↩2
-
Cloud Seed GitLab Page – GitLab’s handbook entry for Cloud Seed. ↩
-
Cloud Seed Documentation – Official Cloud Seed documentation. ↩
-
Trusted Testers Signup – Join the beta program and provide feedback. ↩
-
mkdocs – A static site generator for project documentation, known for flexible styling and themes. ↩
-
Toastmasters International – Public speaking and leadership training. ↩
-
How to Win Friends and Influence People – Dale Carnegie’s guide to influence and communication. ↩
-
Breaking Through To Executive Course – Ethan Evans’ executive presence program. ↩
-
AWS Systems Manager Features – Official AWS documentation for Systems Manager. ↩
-
Amazon Q Developer – Natural language querying tool for AWS Systems Manager. ↩
-
Wardley Mapping – Strategic mapping tool. ↩
-
Should Teams Use Kanban Instead of Scrum? – Exploration of Kanban vs. Scrum benefits. ↩
-
Can Kanban Be Used with LeSS or Scrum? – Discusses integration of Kanban with large-scale Scrum. ↩
-
Premium PMF Resources – Access guides, templates, and pitch decks. ↩
-
ZenML LLMOps Database – Curated knowledge base for LLM operations. ↩
-
Kalix – Platform for distributed, stateful application development. ↩
-
WebAssembly – Secure, portable execution environment. ↩
-
Apache DataFusion – Query engine leveraging Arrow for fast, distributed processing. ↩
-
Delta Lake – Open table format for analytics and data lakes. ↩